Understanding the Basics
If you're thinking about building a wireless network for your home or office, it pays to do a little planning to ensuree you implement it as securely as possible. Remember how you listened to your next-door neighbor's conversation with her mother-in-law about what happened at last year's 4th of July party on your baby monitor? Like all radio frequencies, anyone with a receiver can tune into a wireless channel, so you need to take extra precautions to prevent to your big-eared neighbor and cybercriminals from listening in.
The primary reason for building a wireless LAN (WLAN) is for increased mobility — so you can move around from room to room without being tethered to a network jack. Another reason people like wireless LANs is because they can network their computers together without having to snake wires through their walls. Since you don't have to deal with the wires, in some regards building a wireless LAN is actually easier than you might think.
There are all different kinds of wireless protocols used for different types of wireless networks, but if you want to build a WLAN for your home or office the type of protocol you'll want to use is called 802.11b. When you build a wireless network, you are basically setting up a transmitter called an access point that has an antenna on one side and a wire on the other. The wire plugs into a typical wired connection — an Ethernet, a DSL line, cable connection, or dial-up modem. The antenna talks to the wireless network interface card on your computer, sending network traffic from your laptop to an access point. If it sounds confusing, think of your cordless phone. On one end your cordless phone plugs into a wire, while at the same time the antenna on the hand-held receiver transmits to the base station where the wire is plugged in.
Set Up Your Access Point
One of the first things you'll need to do is setup a wireless access point (AP). If you're setting up your wireless network for a business, you'll want to use a more fully featured high-end AP like a Cisco Aironet 350 Series access point. If you're setting up an access point for a home network, a low-end access point such as a Linksys WAP 11 or an Apple AirPort will suffice. Any access point worth its salt has a TCP/IP interface whether you are setting it up for your home or office, which is something to keep in mind when making your purchasing decisions.
When setting up your access point, you'll want to first connect it to the wired hub, then configure the wireless interface, then the wired interface, and last but not least, configure the security. Configuration of the various network interfaces and access point features is different for every vendor. However, if you can read and follow directions, it's possible to do the installation yourself, even if you don't have prior experience. Just open the access point installation and configuration guide and follow along. If you run into snags call the vendor support line list in your access point manual and ask for help. The types of things you'll need to setup include the radio frequency, the distance between access points, and the access point IP address.
Some of the features you can expect to find in either home or enterprise class access points are listed in this table:
| Feature | Small Office/Home Office | Large Office |
| IEEE 802.11b compliance |  |  |
| DHCP Server |  |  |
| Network Address Translation |  |  |
| IPSec Pass Through |  |  |
| IAPP |
|  |
| Site Management Tools |
|  |
| WEP (Security) |  |  |
| TKIP (Security) |
|  |
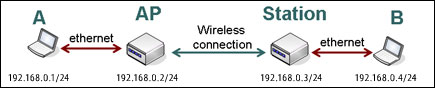
You can also use what is known as a wireless station instead of an access point. However, wireless stations may take a bit more work to setup, and I won't be talking about them further in this article.
Your access point is the link between the wireless world and the wire. So after you setup the wireless interface, you need to setup up the wired end of the connection — the Ethernet interface. When you configure the Ethernet interface, you will select the speed and duplex particulars. For many access points, however, the speed and duplex settings are self-setting.
Set Up Your Laptop
Since the purpose of a wireless network is mobility, it makes more sense to use a laptop (rather than a desktop) to connect to the WLAN. If the purpose of your WLAN is to avoid shoving wires through walls, it's possible that you may want to connect a desktop system or server to the WLAN. For the purpose of this article, we'll use a laptop to get you up and running. Your laptop will need a wireless network interface PCMCIA card. A wireless network interface card made by any reputable company should suffice. Some of the popular ones of the market today that you might want to consider include:
- Agere Wireless LAN PC Card
- Proxim/ORiNOCO Wireless Proxim ORiNOCO 11b Client
- Cisco Aironet 5GHz 54Mbps Wireless LAN Client
Wireless network interface cards have a 48-bit MAC address associated with them that is completely unique to each card. Installing the wireless PCMCIA card is really no more difficult than installing a regular PCMCIA card. In fact, all the new laptops running Windows operating systems should recognize the card and launch a Setup Wizard that will actually guide you through the installation process by prompting you to make certain decisions along the way. You'll need to install the device driver and enter the SSID associated with your access point. Setting Up the Security
If you have a low-end access point, your security will be limited to Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and MAC address filters. With a higher end access point, you'll be able to turn on Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP). WEP is a system for encrypting your data to keep it private from unauthorized users. It was designed to provide privacy equal to what you get on a wired network. TKIP works on top of WEP, offering stronger security than WEP, and increased assurance that your data will not be compromised.
While it has been found that WEP does not offer strong security, it does offer some security, and any security is better than none. Therefore, you should turn WEP on no matter what. You can also layer more security, such as TKIP, on top of it. WEP uses secret keys that get combined with a keystream that then encrypts your data into ciphertext. At the receiving end, a corresponding keystream is used to decrypt the data.
WEP is used to authenticate you to the network and a component of it needs to setup on both the PCMCIA card and on the access point. WEP can be implemented in 40-bit mode or 128-bit mode. As you may suspect, using the 128-bit mode offers more security than the 40-bit mode.
TKIP evolved to solve some of the security problems that WEP does not solve. However, TKIP is relatively new, and many access points and wireless client cards do not support it. If you want to use TKIP, you'll need to be sure you purchase wireless access points and client cards that support it. With WEP, wireless hackers who have the will and time to do so, can obtain the encryption key need to unlock access to the data. In response to the vulnerabilities of WEP, a task group of the IEEE designed TKIP to add stronger security on top of WEP.
TKIP offers new encryption algorithms, and constantly changes the encryption keys making them harder for wireless hackers to capture them. Because the keys are constantly changing, if one of them gets captured, it won't do a hacker much good because by the time they try to use it, the wireless LAN will be using different encryption keys. With TKIP, the encryption keys are also encrypted themselves so you would first need to decrypt the key, before you can use the key to decrypt the network traffic.
MAC address filtering is used to limit what pieces of hardware can access the wireless network. On a large network, filtering the MAC address can be quite an administrative chore and it's worth using cards with sequential MAC addresses to make the job easier. If you want to use sequential MAC addresses, this is something you will need to specify when you make your purchasing decisions. On some wireless PCMCIA cards you can change the MAC address, but on many wireless PCMCIA cards the MAC address is fixed.
For even more security, you can also install a Virtual Private Network (VPN) on your wireless network. Unless you have truly sensitive information, it's probably not worth the time and effort to do this. By using a VPN, you tunnel your wireless data through an IPSec gateway. Using WEP, TKIP, and a VPN together will create a very strong security barrier on your wireless network. Using a VPN can create performance bottlenecks, so don't use one if you don't need one.
Summing It Up
Setting up a secure wireless network is not as hard as it may seem. Anyone with the ability to research wireless product capabilities, and follow the installation instructions can do it. The advantages of not using wires is tremendous, and while some organizations may be reluctant to use wireless networks today, in time they will become ubiquitous and wires will become history.
![]()
![]()
![]()







